“The important thing is to never stop questioning.” – Albert Einstein
Key information:
GCSE Specification
A Level Specification
Curriculum Progression
At Key Stage 3, we have a spiral curriculum which allows topics to be revisited each year. This gives students the foundations on which to build a deep knowledge and fully prepare them for GCSE content.
Key Stage 3
Year 7
Students begin the year with an Introduction to Science week which will provide them with the basic skills and knowledge of how to work and learn safely in a laboratory. They then begin with the chemistry topic matter, in which students learn about states of matter, atoms through to compounds, mixtures and how to separate them. Students then move onto learning about reactions with acids, bases, metals and non-metals. After half-term students move onto the physics topics forces and energy. Students will learn about forces, including gravity, and their effects, as well as how electricity is produced and the law of conservation of energy. After Christmas students move onto biology topics organisms, genes and ecosystems. Students learn about cells and how they work together to form organisms. Students will move onto variation between organisms by learning about species and both human and plant reproduction before looking at the interdependence between organisms in the ecosystems topic. Before the end of the year students will revisit physics and the electromagnetics topic, learning about electricity and circuits. Having looked at the smallest parts of the universe at the start of the year, students will now study the structure of the Earth and the solar system in another chemistry topic, earth, before lastly moving onto waves and learning about light, sound and how we see and hear the world around us.
Year 8
Because of the spiral curriculum; students in Year 8 will study the same topics as in Year 7 but will build on the foundations of knowledge they developed last year whilst learning new content.
Students will revisit the topic forces to learn in more detail about contact, non-contact and resultant forces and pressure in fluids whilst applying this to the context of hydraulics. When revisiting matter students will learn about the structure and patterns of the periodic table and learn how to name and write chemical formulae for the compounds they learnt about the year before. Students will learn more about reactions whilst studying reversible and irreversible reactions and be able to write equations for these reactions. Building on the knowledge of cells and organisms from Year 7, students will learn about breathing and digestion in the organism topic before learning about respiration and photosynthesis in the ecosystems topic. In the second half of the year students will revisit energy and waves to learn about energy transfer by heating, properties of waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. When students revisit the earth topic students will learn about the cycle of resources in the carbon cycle and the impact of global warming and climate change. Students will finish the year revisiting the genes topic to learn about the theory of natural selection, biodiversity and genetics and inheritance.
Year 9
In year 9, students begin to study science in the three separate subject areas: biology, chemistry and physics.
Biology:
The students will gain an understanding of cells in terms of how they are structured and organised. They will look at how cells divide and grow through the cell cycle and how substances move in and out cells. Towards the end of year 9 the students will start to look at some important processes in both plants and animals with a focus on respiration and photosynthesis.
Chemistry:
In year 9 student begin by looking at fundamental concepts. Students begin the year by looking at the periodic table. They then move on to study how energy changes occur during a chemical reaction and they finish by looking at chemical changes.
Physics:
Students will begin by looking at how the worlds energy resources are harnessed and utilised, understanding which sources are reliable, and renewable, along with their short and longer-term environmental impacts. Students then explore the concept of energy changes. They will then move on to consider waves are one the ways that energy can be transferred, and students will learn about the properties of different types of waves, including investigations into the waves in light, sound and water.
Key Stage 4 (GCSE)
Biology
Year 10 Triple:
In year 10, the students will be building on their knowledge to work towards being successful in their GCSEs. The students start the year looking at infection and response, they will gain an understanding of communicable and non-communicable diseases, how diseases are spread, ways in which you can stop the spread of diseases and how diseases are treated. They will also gain an understanding of different types of medicine and how new medicines are discovered and developed. They will then further develop their knowledge of the body’s process by looking at the nervous system and hormonal communication. They will finish year 10 by looking at biodiversity and ecosystems looking at habitats and how organisms are adapted to the environments they live in.
Year 11 Trilogy:
In year 11, the focus will be around consolidating knowledge from both year 9 and 10 whilst also looking to further develop understanding on new topics and concepts. The topics covered in year 11 start with reproduction, variation and evolution. They start by looking at reproduction in both plants and animals and clearly to be able to explain how these organisms reproduce. In term 2 the students will look at variations in species, how species have evolved and their genetic makeup. They will then move onto revision to allow them to be in the best possible place for their upcoming exams.
Year 11 Triple:
Students start by exploring Biodiversity and reproduction in plants and animals. Later in the years students learn how variation can be produced through reproduction and how evolution has lead to changes in living organisms over time.
Chemistry
Year 10 Triple:
In year 10, the students will be building on their knowledge to work towards being successful in their GCSEs. The students start the year looking at further develop their understanding about the fundamentals of matter and what atoms are made from and how and why this impacts on how they can create compounds by forming chemical bonds. They then look at atoms again and the essential mathematics of quantitative chemistry that is central to industrial chemical processes. During the spring term students investigate chemical changes practically and how energy changes occur during chemical reactions. Students return to the study of atoms and ions to learn how compounds can be separated using electricity during electrolysis. Students finish the year by exploring the factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions.
Year 11 Trilogy:
In year 11, the focus will be around consolidating knowledge from both year 9 and 10 whilst also looking to further develop understanding on new topics and concepts. The topics covered in year 11 start with the crude oils and fuels topics, where students learn how crude oil is made useful through fractional distillation. Students then study chemical analysis and learn about different methods used to analyse chemical in the laboratory. Students finish their GCSE by learning about the resources that we have and how they are used, including where our drinking water comes from.
Year 11 Triple:
Students begin the year by exploring organic chemistry. Students learn about crude oil and its use in the petrochemical industry. Students explore organic reactions and how polymers can be made. In the spring term students look at chemical analysis and learn about different methods used to analyse chemical in the laboratory. Students finish the year by learning about the earth’s resources and how we as humans can help create a more sustainable future.
Physics
Year 10 Triple:
Students in year 10 begin by looking at electrical circuits which they first studied in Key Stage 3. They will learn to build, test and analyse their own circuits as well as learning about electricity in the home and how the electricity from power stations is distributed. They will build on the previous year’s energy studies by looking at measuring thermal energy transfers plus work on insulation and energy efficiency. In particle physics, students will understand the nature of matter, state changes, gas pressure and density before moving on to look at the structure of the atom and how scientific understanding of sub-atomic particles developed. They will then proceed to study radioactive decay, its uses and dangers. In mechanics, the actions of forces on objects will be analysed before moving on to study motion: including displacement, velocity and acceleration along with Newtons laws.
Year 11 Trilogy:
In the final year of GCSE physics, students will develop their understanding of electromagnetic waves further by looking at the properties and uses of the complete spectrum. Students will also explore waves and their properties.
Year 11 Triple:
In the final year of GCSE physics, students will develop their understanding of electromagnetic waves further by looking at the properties and uses of the complete spectrum. Triple science students will also look at additional wave properties including further studies of sound waves, analysis of black body radiation and reflection of light. Students will learn about solenoids, electromagnets and the motor effect in the electromagnetism topic along with how to calculate the strength of magnetic fields. Triple science students will also study transformers and the generator effect. Astrophysics will also be studied by those pupils taking triple science. This includes looking at the solar system and the lifecycle of stars, understanding orbital motion and seeing how redshift shows us the expanding universe.
Key Stage 5 (A Level)
At Key Stage 5, students can choose from a variety of courses.
Biology (A Level)
The course begins with a focus on photosynthesis and respiration. Students learn about the mechanisms behind the two processes, this requires them to prove the mechanisms using key practical techniques. Students then move onto how the body responds internally and externally to stimuli. The topic focuses on the workings of the nervous system and how the body sends chemical messages through homeostasis to control blood sugar levels and water balance. The next topic is all about how variations in genes form the basis for evolution. Students start by looking at how alleles are inherited independently and then in combination. Once that knowledge is secure, the course focuses on population genetics and how new species arise thought genetic variation, selection of the best suited genes and genetic drift. This knowledge formed the basis for the theory of evolution by natural selection. Finally, students study how genes can be manipulated for human benefit. Students learn in detail the process of genetic modification and the ethical dilemmas this branch of science produces. The course ends with a focus on forensic science. Students study forensic techniques such as DNA analysis and PCR testing.
Chemistry (A Level)
Through A Level chemistry, students will be developing essential knowledge and understanding of different areas of the subject and how they relate to each other. It will also improve and demonstrate a deep appreciation of the skills, knowledge and understanding of scientific methods. Students will build on GCSE topics such as chemical reactions, chemical bonding and earth science to study inorganic, organic and physical chemistry in more detail. This course overall will nurture a passion for Chemistry.
Physics (A Level)
Students will already be familiar with many of the topics that they will study at A Level physics from their GCSE studies, including forces, waves, radioactivity, electricity and magnetism. At A Level, students look at these areas in more detail and find out how they are interconnected. They will also learn how to apply maths to real-world problems and explore new areas such as particle physics and astrophysics. Throughout the course, students will carry out practical activities including the use of lasers and the safe use of ionising radiation allowing them to develop mastery of the practical skills needed to carry out successful experiments in their degree.
Applied Science (Level 3 Certificate)
This course develops your understanding of scientific theory and skills, and coupled with experimental techniques helps you to become a well-rounded scientist. Over the course of the two years, students will study a range of biology, chemistry and physics based subjects which include:
- Human Physiology
- Microbiology
- Genetics and Genetic Engineering
- Astronomy and Medical Physics
Throughout the course, students will have the opportunity to perform a variety experimental work, learn how to work safely within a laboratory environment and to use maths and statistics to analyse experimental data.
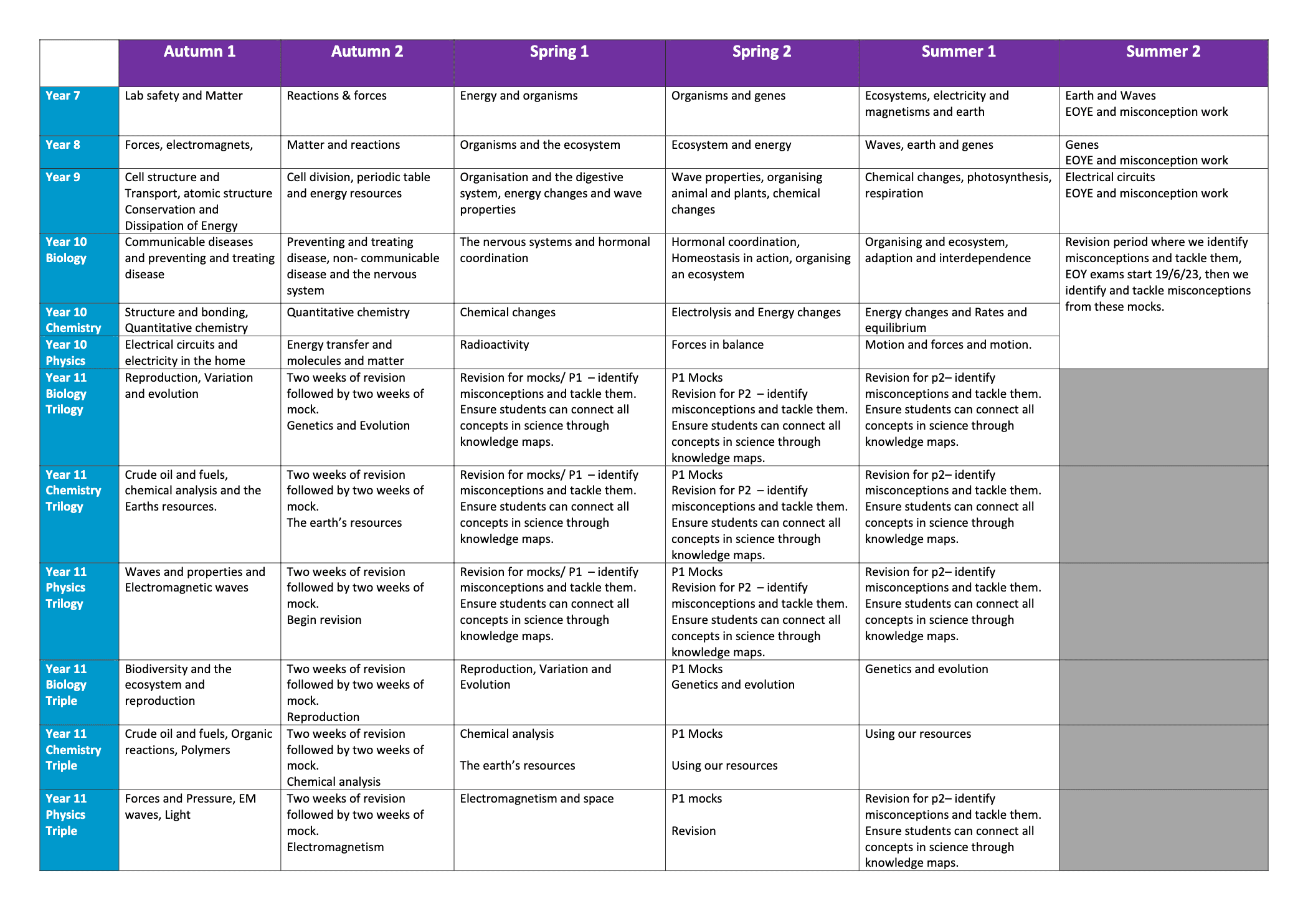
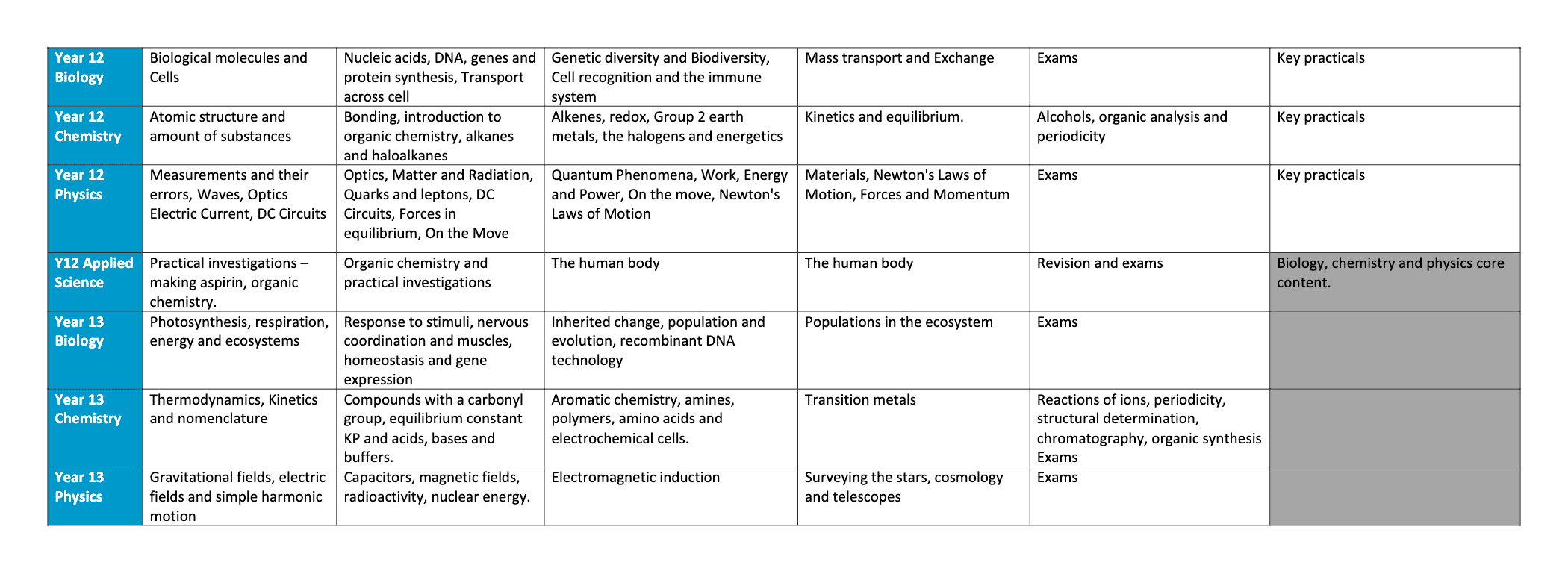
Curriculum Map